Anatomy
Français / English
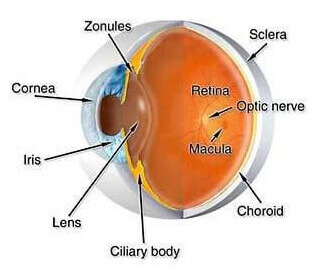
Zonules
The fiber-like processes extending from the ciliary body to the capsule of the lens of the eye. The zonules are responsible for holding the lens of the eye in its normal position.
Sclera
The white outer wall of the eye.
Cornea
The front clear “window” of the eye (where a contact lens rests). The cornea is responsible for focusing light rays to the back of the eye.
Retina
The layer of tissue lining the inside of the back of the eye. The retina contains millions of photoreceptor cells which convert light into images.
Macula
The center of the retina which is responsible for about the central 15 degrees of vision. The macula is approximately 5.5mm (less than 1/4 inch) in diameter.
Optic Nerve
The bundled collection of the retinal nerve fiber layer which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain.
Iris
The colored structure which rests behind the cornea and in front of the natural lens. The opening in the center of the iris is the pupil. The iris acts like a camera shutter and controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Lens
Normally clear, the lens sits behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor. The lens focuses light rays on the back of the eye.
Ciliary Body
Located just behind the iris, the ciliary body is instrumental in controlling focusing of the eye and the production of aqueous fluid.
Choroid
A vascular layer situated between the retina and the sclera of the eye.

